At present, semiconductor technology has been developing rapidly, so the power consumption and size of radar have been reduced greatly and its function is getting stronger by using multiple transmission and receptions, ultra-wideband technology, millimetre-wave, signal processing technology, integrated circuits with increasing computing capabilities, etc. Traditional radar is widely used in applications such as shipborne, base radar, airborne, etc., whereas a radar sensor is used in our daily life to obtain weather forecasts, resource surveys, traffic control, etc. This sensor is a conversion device, used to change the microwave echo signals into electrical signals. Therefore, this article discusses an overview of a radar sensor and its working.
1.What is Radar Sensor?
The sensor which is used to measure the distance, velocity and movements of objects above wide distances is known as a radar sensor and also measures the relative speed of the noticed object. This sensor uses wireless detecting technology like FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) to detect the motion by figuring out the object’s shape, position, motion trajectory & motion characteristics.

As compared to other types of sensors, these sensors are not affected by darkness and light. These sensors can detect longer distances and they are safe for people and animals. Here, the carrier frequency is modulated constantly within a small range of bandwidth. Once the signal from an object is reflected back, it is possible to determine the distance and also the object's speed by comparing frequencies.
This sensor uses an extremely high carrier frequency to produce a very thin beam cone and also notices even small objects without interference from adjacent objects above large distances.
2.Radar Sensor Working Principle
The working principle of a radar sensor is to compute the speed of an object along with its direction by detecting the change in frequency wave which is known as Doppler Effect.
A radar sensor includes an antenna that emits a high-frequency (62 GHz) transmitted signal. This transmitted signal also includes a modulated signal with a lower frequency (10 MHz). This sensor gets the signal once it is returned back from an object. So this sensor evaluates the phase shift between the two frequencies. Here, the difference in transmitting time & receiving time will determine the distance between the sensor & an object.
3.Radar Sensor Block Diagram
The block diagram of the 24 GHz wideband & short-range automotive radar sensor is shown below. This block diagram includes a VCO, PRF (pulse repetition frequency), LNA (low noise amplifier), DSP (digital signal processing) & two antennas.
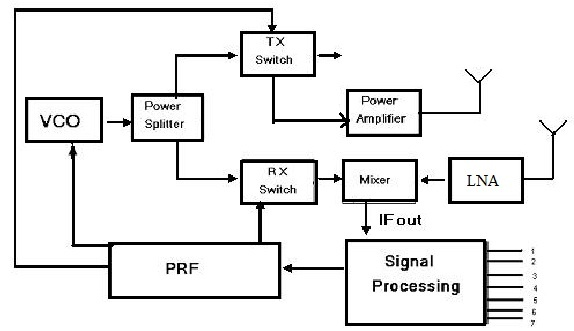
Automotive Radar Sensor Block Diagram
4.VCO
The term VCO stands for voltage-controlled oscillator which is used to generate an o/p signal whose frequency changes with the amplitude of voltage for an input signal above a reasonable frequencies range.
5.Power Splitter
A power splitter or power divider is used to divide a single RF line into above one line & split the power.
6.Power Amplifier
A power amplifier is used to change a signal from a low-power to a higher power.
7.SP (Signal Processing)
Signal processing focuses on modifying, synthesizing & analyzing signals like images, sound, & scientific measurements.
8.PRF (Pulse Repetition Frequency)
The pulse repetition frequency is the number of pulses of a repeating signal within a specific unit time, usually measured in pulses for each second.
9.Mixer
The mixer is used to generate both the frequencies sum & difference which are applied to it. So the frequencies difference will be of IF (Intermediate Frequency) type.
10.LNA (Low Noise Amplifier)
It is used to amplify the weak RF signal and this signal is received by using an Antenna. This amplifier’s output can be connected to Mixer.
11.Antennas
This system includes transmit & receive channels where the transmit channels are mainly used to drive different antennas & also provide beam steering capabilities. Multiple receive channels provide the angular data regarding the target because there is a phase difference between received signals by dissimilar receive antennas.
The concept used by the 24 GHz SRR (Short Range Radar) sensors is pulsed radar. This sensor includes the transmitting & receiving path, the control & DSP (digital signal processing) circuits.
The target at range ‘R’ can be detected by measuring the elapsed time in between a transmitter signal & a correlated received signal. The simulation process was done using Matlab. The main aim of this radar sensor is to decrease potential danger & traffic accidents faced by the vehicle driver. In this system, different sensors are located in different places of the car so that the exact measurement of object distance & speed of objects in front, behind, or beside.
Every sensor in this system transmits the signals to calculate, if there is anybody in the region of the car then informs the driver regarding it. These signals cover upto 30 m distance but, if the distance in between the target & car was less than two meters, then the car generates an alarm sound to give an alert to the driver so that the car driver can take the appropriate action to avoid a collision.
12.Radar Sensor Types
Radar Sensor Vs Ultrasonic Sensor
The difference between the radar sensor and the ultrasonic sensor includes the following.
Feature | Radar Sensor | Ultrasonic Sensor |
Functional Description | Used to convert microwave echo signals into electrical signals. | Used to measure the distance to an object using ultrasonic sound waves. |
Working Principle | Operates with electromagnetic waves. | Operates by generating sound waves. |
Wave Propagation & Reflection | Similar to ultrasonic waves, the waves emitted by this sensor reflect off the target and travel at a known high speed. | Sound waves travel at the speed of sound to the target, reflect off it, and return to the sensor. |
Response to Materials | Its electromagnetic waves respond differently to specific materials as they are reflected off the surface. | Its sound waves do not respond to specific materials. |
Affected Variables | Affected by various variables. | Affected by temperature. |
Application Fields | Used in oil & gas, pulp & paper, clarifiers, granular solids, plastic pellets, pharmaceuticals, etc. | Used for measuring liquid flow, solids level, open-channel flow, object profiling & presence detection. |

Radar sensors

Ultrasonic sensor
13.Advantages
The advantages of radar sensors include the following.
- The radar sensor is independent of different weather conditions
- Bears excessive cold & heat
- It works in bad lighting conditions
- It works in the dark
- Its maintenance is free
- It provides a great range of functions
- This sensor is used for indoor & outdoor purposes
- This sensor has many features as compared to other sensors
14.Disadvantages
The disadvantages of radar sensors include the following.
- It cannot differentiate & resolve numerous targets which are extremely close like our eye.
- It cannot identify the color of the objects.
- It cannot observe objects which are too deep and in the water.
The applications of radar sensors include the following.
- Radar sensors are used where vehicle detection is required or avoiding a collision when equipment is moving. Vehicle detection mainly includes trucks, trains, cars, toll booths, shipping canals, railroads, etc. Collision avoidance includes ports, manufacturing, low-visibility factory environments & onboard mobile equipment.
- Military
- Security system
- Automotive electrons
- Intelligent traffic radar
- UAV radar
- Intelligent lighting
- Industrial control
- Medical treatment
- Sports
16.What does a radar sensor do?
The radar sensor is used to detect, track, locate, and identify various types of objects at significant distances. This sensor works by transmitting electromagnetic energy to targets & detects the echoes that come back from them.
17. What are the 5 main components of radar?
The five main components of radar mainly include an antenna, transmitter, receiver, diplexer, and phase-locked loop.
18.Why is it illegal to have a radar detector?
In certain countries, using a radar detector is illegal, because it may result in fines, seizure of the vehicle.
19.Can radar detect humans?
Radar cannot detect humans who are walking or stationary across the field of radar but the radar can simply detect the motion components.
20.What causes a dead zone for radar?
The curvature of the earth may avoid the radar detecting an objective in the maximum range, so it results in a dead zone for each radar system where one object can’t be detected. But in the atmosphere of earth, electromagnetic waves are usually refracted downward or bent.
21.What happens if you get pulled over with a radar detector?
If drivers get pulled over with a radar detector for speeding & are found a radar detector in the vehicle then a speeding ticket will be issued by cops.
The advancements in radar sensor using mmWave technology provides flexibility & high accuracy for several in-cabin monitoring applications while delivering a tiny form factor that can be included simply & modestly within a vehicle.
Thus, this is all about an overview of a radar sensor and its working with applications. This sensor uses wireless sensing technology to discover and extract the target’s shape, position, motion, etc. As compared to other types of sensors, these sensors have many advantages. For instance, as compared to the visual sensor, the radar sensor is not affected by darkness and light. This sensor can penetrate obstacles. Similarly, with ultrasound technology, this sensor can detect longer distances without harming animals and people. Here is a question for you, what is the radar sensor range?

