Are you tired of constantly replacing batteries in your IoT devices? Do you have a collection of temperature sensors that barely function due to limited range? Well, LoRa Technology might be the answer to your prayers! This revolutionary technology has made IoT devices a global phenomenon. With their long-range and low-power communication capabilities, they make life easier for anyone concerned with temperature, from farmers to healthcare professionals. Join me on this blog as we delve deeper into the benefits, operating principles, and popular applications of LoRa temperature sensors.
1.What is LoRa Temperature Sensor
A LoRa temperature sensor is a wireless device that uses long-range, low-power radio frequency technology to monitor and transmit temperature readings over long distances. A notable feature of this technology is its low power consumption, allowing for seamless data transmission up to 10 kilometers in rural areas and 2 kilometers in urban areas. LoRa temperature sensors come in a variety of forms, including standalone devices or sensors embedded in devices or systems.
2.LoRa Temperature Sensors: How They Work
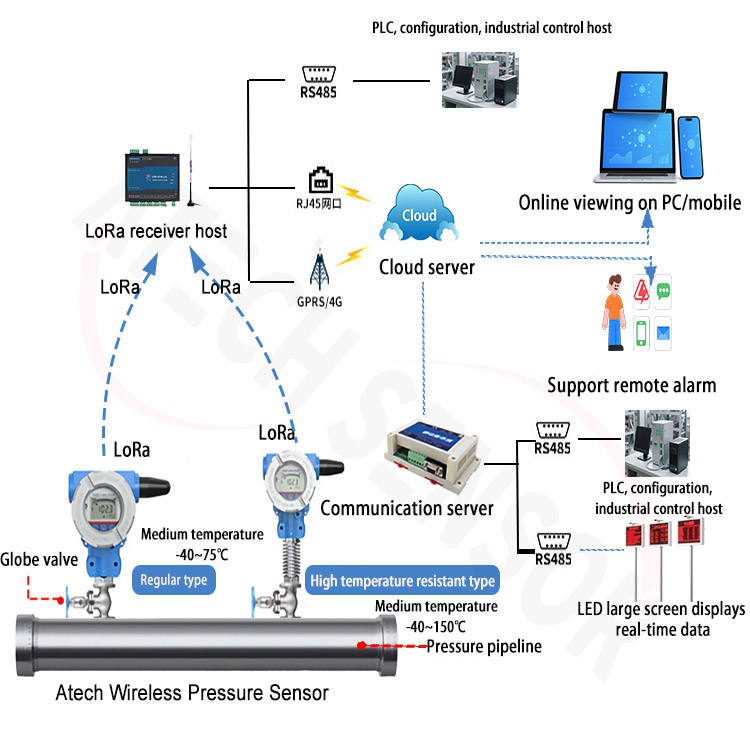
A LoRa temperature sensor consists of two main components: a temperature sensor and a LoRa radio transceiver. The temperature sensor measures the temperature and sends the reading to the LoRa radio transceiver. The LoRa radio transceiver then converts the data into a LoRa signal and transmits it to a LoRa gateway or base station. The gateway receives the signal, converts it into a data packet, and sends it to a server or cloud-based platform. The data can be accessed and analyzed in real time using a computer, mobile phone, or tablet.
3.LoRa Temperature and Humidity Sensor Use Cases
The LoRa temperature and humidity sensor is a valuable and adaptable device with a variety of applications across different industries. Its popularity stems from its cost-effectiveness, long-range transmission, and low power consumption. These features make it a popular choice across numerous industries. Some use cases for LoRa temperature and humidity sensors include:

Agriculture and breeding
Farmers can use LoRa temperature and humidity sensors to monitor temperature and humidity levels in crops, greenhouses, and livestock buildings. This helps farmers optimize growing environments and prevent crop and animal losses due to adverse environmental conditions.
Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial manufacturing can benefit from LoRa temperature and humidity sensors to measure environmental conditions in manufacturing plants and equipment rooms. These sensors can help optimize production processes, troubleshoot problems, and prevent potential delays or downtime.
Food and beverage industry
In the food and beverage industry, it's essential to track product storage conditions. LoRa temperature and humidity sensors help maintain optimal conditions, preventing spoilage and preserving product freshness and quality.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
LoRa temperature and humidity sensors can be used in the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors to monitor temperature and humidity levels in laboratories, clinics, and hospitals. This helps ensure that medications and vaccines are stored in optimal conditions while ensuring their efficacy.
Supply Chain and Logistics
For supply chain and logistics, LoRa temperature and humidity sensors can help monitor the condition of temperature-sensitive goods during transportation. Shipments containing perishable goods can be monitored and tracked to ensure product quality is maintained throughout the shipping process.
Building Automation and HVAC Systems
The application of LoRa temperature and humidity sensors extends to building automation and HVAC systems. By incorporating smart temperature sensors, facility managers can monitor environmental conditions and adjust to changes in temperature and humidity. This helps optimize energy consumption and maintain a comfortable indoor environment for occupants.
4.Advantages and limitations of LoRa temperature sensors
Now that we've covered the various applications of LoRa temperature sensors, it's time to understand their capabilities and limitations . Understanding these factors can help maximize their advantages and minimize potential drawbacks in their applications. Here are some of the benefits of LoRa temperature sensors:
Widely used in various industries, including agriculture, building automation, and HVAC systems.
High cost performance, low power consumption, allowing long-lasting battery life.
Long-range transmission capability of up to several kilometers, suitable for monitoring wide locations without the need for additional repeaters.
Real-time data monitoring, rapid detection of temperature and humidity changes, and early warning to optimize the environment to achieve the desired results.
Despite their advantages, LoRa temperature sensors also have some limitations .
Low power consumption sometimes comes at the expense of reduced data bandwidth, resulting in limited data transmission for high-precision applications.
The available sensing range can be a limitation, with some models unable to measure extreme temperatures and humidity levels.
The accuracy of the readings may be affected by signal interference, increasing the possibility of false readings.
While LoRa sensors are cost-effective, integration with other systems may incur additional costs, such as sensor gateways and backend servers.
5.conclusion
Comprehensively, LoRa and LoRaWAN temperature sensors offer the best of both worlds: they're wireless, highly secure, and provide long-range connectivity. They're ideal for monitoring temperature in hard-to-reach environments and areas where conditions frequently change. As more and more industries adopt LoRa temperature sensors, it's clear we're witnessing the future of temperature monitoring. Now's the time to invest in this innovative technology to ensure your devices and products always maintain the right temperature.

